
Soldier Performance
From armor and exoskeletons that reduce a wearer’s muscle fatigue to learning how to interact with farm animals, NC State’s research and training offer both hard and soft skills development opportunities for soldiers to improve their performance in the field. Our deep bench of experience in biomedical engineering, 3D printing/tissue manufacturing, rehabilitative medicine, prosthetics, mental health, global health security and disease reduction creates opportunities for health improvement and harm reduction for our troops and the communities they serve.
NC STATE FEATURED STORIES

Soldiers In The Field
Read more

Researchers Fix ‘Fundamental Flaw,’ Improving Pandemic Prediction Model
Read more
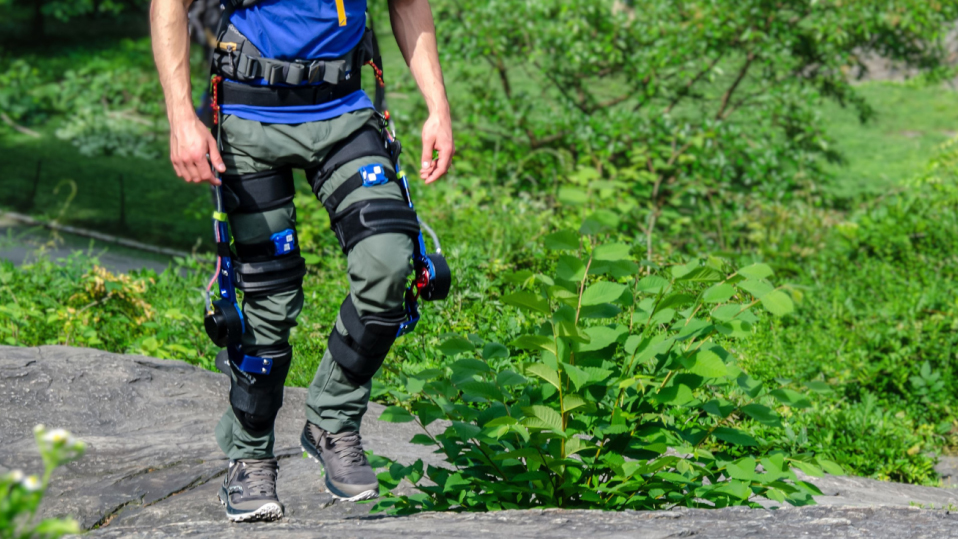

MAE Researchers Develop New Lightweight Exoskeleton
Read more

Mitigating Mental Health Issues From Combat Exposure
Read more
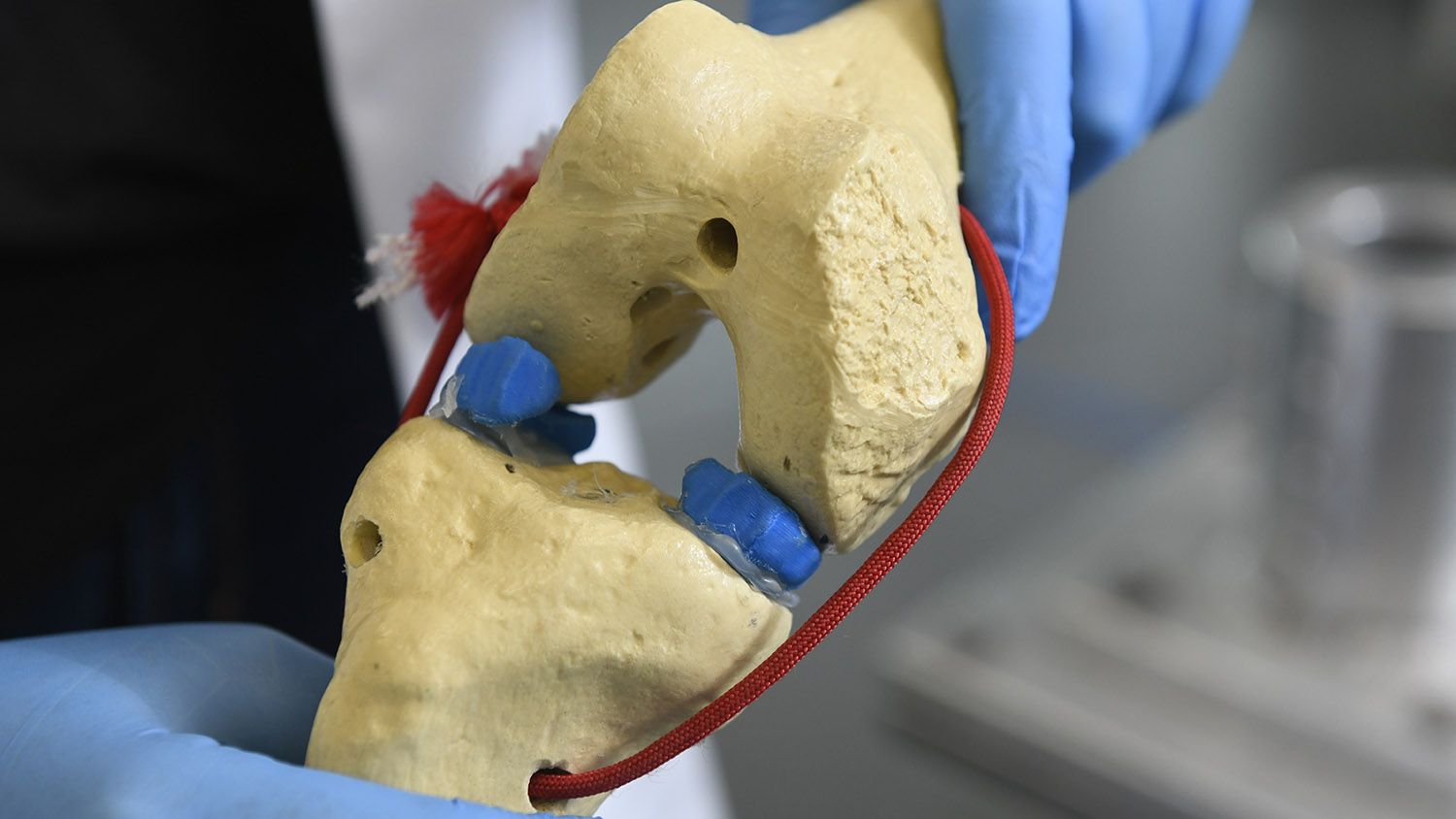
A Revolution in Regenerative Medicine — Led by NC State
Read more

Solving Health Crises for a Better World
Read more
Centers, Institutes, Labs and Facilities
Center for Advanced Self-Powered Systems of Integrated Sensors and Technologies (ASSIST)
Wearable technology can monitor an individual’s health and help prevent casualties during military training, by spotting health problems before they become critical. ASSIST focuses on creating self-powered sensing, computing, and communication systems to enable data-driven insights. ASSIST brings together researchers, practitioners, and industry partners in a diverse and inclusive ecosystem that encourages innovation with a focus on education and outreach. The center develops systems for high-value applications by integrating fundamental advances in energy harvesting, low-power electronics, and sensors with a focus on usability and actionable data.
Movement Biomechanics Laboratory (MoBL)
MoBL improves the function and treatment of neuromusculoskeletal injury in the upper limbs through an improved understanding of musculoskeletal structure-function relationships.
Vector Borne Disease
The focus of the Vector Borne Disease Lab at NC State is research to benefit animal health. It is our intention to provide quality answers to diagnostic questions. The assays, antigens and controls used are developed and validated as a component of our research. We modify methods or reagents as needed to achieve the best analysis possible without reliance on any proprietary methods or reagents.
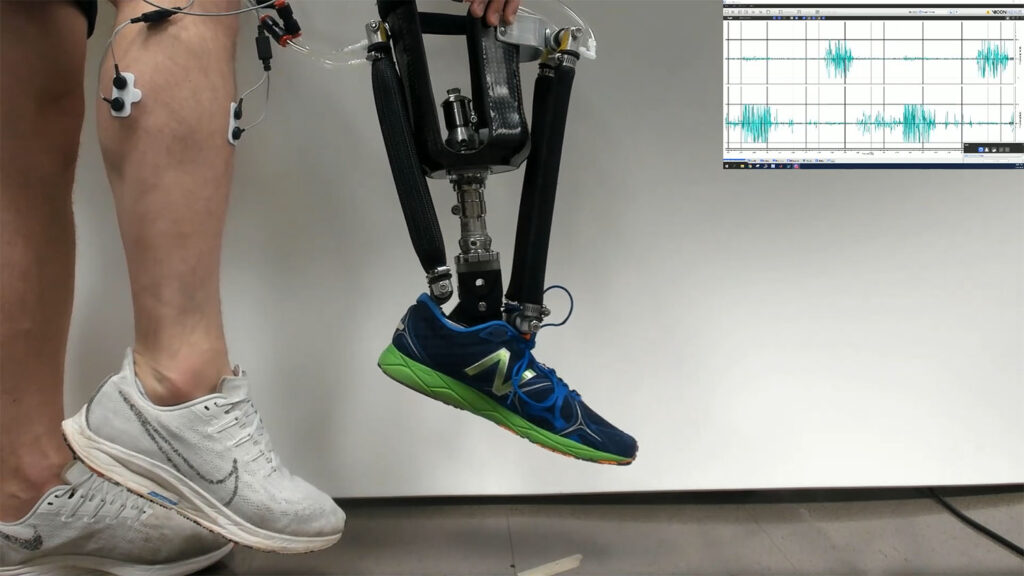
Robotic Prosthetic Ankles Improve ‘Natural’ Movement, Stability
Education
Biomedical Engineering (BME)
Biomedical engineering, a joint department with UNC-Chapel Hill, works to change the world through medicine, engineering and technology.
Global One Health Academy
Through its partnerships, interdisciplinary faculty expertise, research, and engagement activities, the Global One Health Academy promotes worldwide health equity and tackles shared health threats by looking at all angles — plant, animal, biodiversity, environmental and human.
K-9 Down
Offered by the vet school, this course is tailored for military dog handlers, police officers, firefighters, medics, and search and rescue teams. Students learn treatment for when dogs suffer from smoke inhalation, burn wounds, heat stroke and hypothermia, gunshot wounds, poisoning, broken bones, internal injuries, and other issues.
